Chromatin Condenses into Chromosomes: Unraveling the Intricacies
Chromatin, the complex of DNA, RNA, and proteins within the nucleus, plays a pivotal role in cellular functions. One of the fascinating processes involving chromatin is its condensation into chromosomes. This article delves into the intricate mechanisms of chromatin condensation, exploring its significance in cell biology.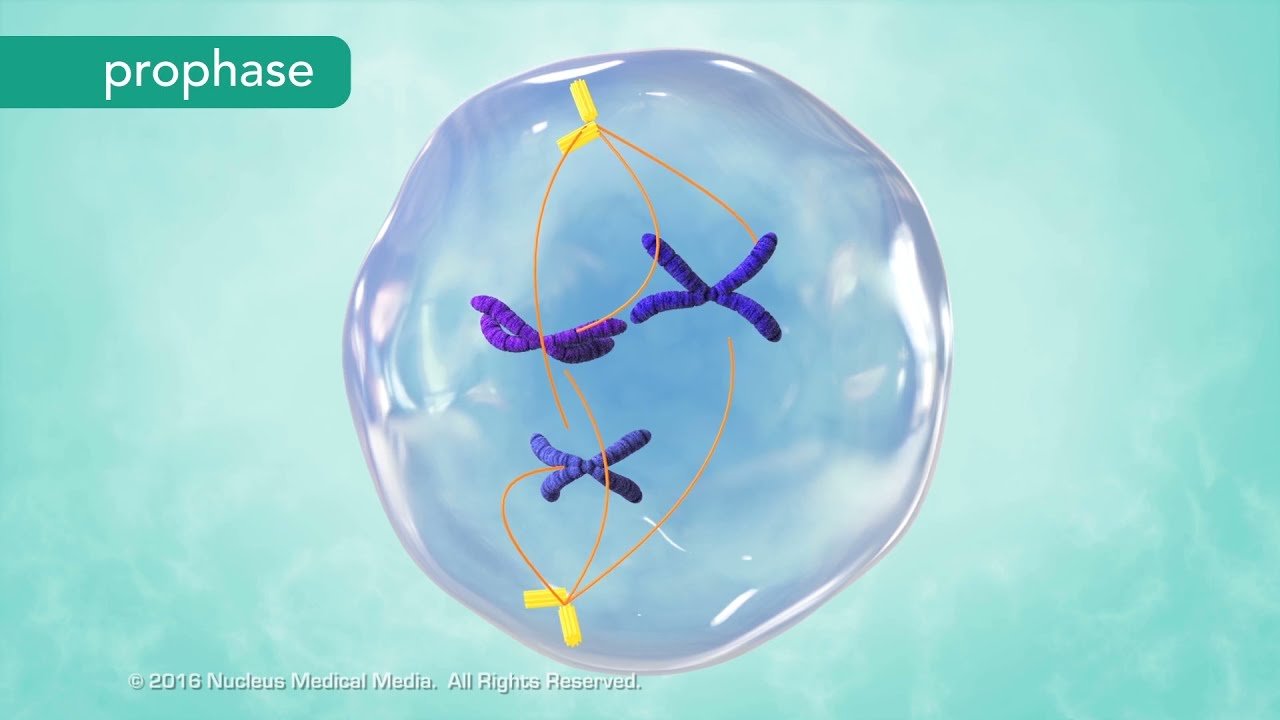
I. Introduction
Definition of Chromatin
Chromatin, the substance of a cell’s nucleus, comprises DNA, RNA, and proteins. Understanding its structure is crucial to comprehend the dynamics of genetic material within cells.
Significance of Chromatin Condensation
The condensation of chromatin into chromosomes is a fundamental event in cell life. This section explores why this process is essential for various cellular functions.
II. Chromosome Formation
Process of Chromatin Condensation
1. Role of Histones
Histones are key players in the condensation process. Unraveling their role sheds light on the compacting mechanism of chromatin.
2. DNA Wrapping Mechanism
How DNA is intricately wrapped around histones forms the basis of chromosome formation. Delve into the details of this fascinating process.
III. Key Players in Chromatin Condensation
Histones
Understanding the types and functions of histones provides insights into the regulation of chromatin structure.
Non-histone Proteins
Beyond histones, non-histone proteins contribute significantly to chromatin condensation. Explore their roles and significance.
IV. Importance in Cell Division
Chromosome Segregation
The condensed chromosomes ensure accurate segregation during cell division. Learn how chromatin condensation safeguards the fidelity of genetic material distribution.
Ensuring Genetic Stability
Chromatin condensation is crucial for maintaining genetic stability. Discover the mechanisms that prevent errors during DNA replication.
V. Regulation of Chromatin Condensation
Cell Cycle Control
The tight regulation of chromatin condensation is intricately linked to the cell cycle. Uncover the checkpoints that govern this process.
Impact of Environmental Factors
External factors influence chromatin dynamics. Explore how environmental cues can modulate chromatin condensation.
VI. Diseases Associated with Chromatin Abnormalities
Cancer
Chromatin abnormalities are linked to various cancers. Understand the connections between chromatin condensation and cancer development.
Genetic Disorders
Certain genetic disorders result from aberrations in chromatin structure. Explore the implications for inherited diseases.
VII. Technological Advances in Studying Chromatin
Microscopy Techniques
Cutting-edge microscopy techniques enable scientists to observe chromatin condensation at unprecedented resolutions.
Genomic Approaches
Genomic methods provide a holistic view of chromatin dynamics. Learn how these approaches contribute to our understanding of chromatin biology.
VIII. Evolutionary Perspectives on Chromatin Condensation
Conserved Mechanisms
Chromatin condensation is a conserved process across species. Explore the evolutionary aspects that underline its importance.
Adaptations in Different Species
While the process is conserved, different species exhibit adaptations in chromatin condensation. Unravel the diversity in this fundamental biological event.
IX. Future Implications and Research Directions
Therapeutic Applications
Insights into chromatin condensation open avenues for therapeutic interventions. Explore potential applications in medicine.
Unexplored Avenues in Chromatin Research
Despite advancements, certain aspects of chromatin condensation remain unexplored. Delve into the areas that warrant further investigation.
X. Conclusion
Chromatin condensation into chromosomes is a marvel of cellular biology. This article has journeyed through the intricacies of this process, highlighting its significance, regulatory mechanisms, and implications for health and disease. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of chromatin, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries in the field remains immense.
FAQs
- What is the primary function of chromatin within a cell?
- Chromatin serves as the complex of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus, playing a vital role in genetic information storage and regulation.
- How does chromatin condensation contribute to genetic stability during cell division?
- Chromatin condensation ensures accurate chromosome segregation, preventing errors in genetic material distribution.
- Are there specific environmental factors that influence chromatin condensation?
- Yes, external cues can modulate chromatin dynamics, impacting the overall structure and function.
- What role do non-histone proteins play in chromatin condensation?
- Non-histone proteins significantly contribute to the process, influencing chromatin structure and function.
- How can insights into chromatin condensation be applied in therapeutic settings?
- Understanding chromatin dynamics opens avenues for therapeutic interventions, potentially influencing disease treatment and prevention.